Planning-碰撞检测之分离轴定理(SAT)
原文:dyn4j-SAT (Separating Axis Theorem)
目录
- 1. 原理
- 2. 分离轴
- 3. 凸多边形在分离轴的投影
- 4. 计算MTV
sat(分离轴定理)用来检测两个凸多边形是否相交,也可以用于检测点是否在凸多边形内。凸多边形内的点的连线上的点都在凸多边形内,或者连线只和图多边形相交两次(边界处)。


1. 原理
如果凸多边形在某个轴上的投影不重叠,则两个凸多边形不相交。需要对所有的轴(每个边的法向量)进行投影,存在一个轴上的投影不相交,则两个凸多边形不相交。如果所有轴上的投影都相交,则多边形相交。


Axis[] axes = // get the axes to test
// loop over the axes
for (int i = 0; i < axes.length; ++i) {Axis axis = axes[i];// project both shapes onto the axisProjection p1 = shape1.project(axis);Projection p2 = shape2.project(axis);// do the projection overlap?if (!p1.overlap(p2)) {// the we can gurantee that the shapes do not overlapreture false;}
}
// if we get here then we know that every axis had overlap on it
// so we can guarantee an intersection
return ture;
2. 分离轴
分离轴是凸多边形每个边的法向量。做碰撞检测的两个凸多边形的所有边都需计算其法向量。如果只需要计算两个凸多边形是否碰撞,则分离轴不需要归一化;如果需要计算 M T V MTV MTV( M i n i m u m Minimum Minimum T r a n s l a t e Translate Translate V e c t o r Vector Vector,使两个凸多边形不碰撞的最小向量长度),则分离轴必须归一化。
Vector[] axes = new Vector[shape.vertices.length]
// loop over the vertices
for (int i = 0; i < shape.vertices.length; ++i) {// get the current vertexVector p1 = shape.vertices[i];// get the next vertexVector p2 = shape.vertices[i + 1 == shape.vertices.length ? 0 : i + 1];// subtract the two to get the vectorVector edge = p1.subtract(p2);// get either perpendicular vectorVector normal = edge.perp();// the perp method is just (x, y) => (-y, x) or (y, -x)axes[i] = normal;
}
3. 凸多边形在分离轴的投影
计算凸多边形所有顶点与分离轴的点乘,其最大值和最小值就是凸多边形在分离轴上的投影
double min = axis.dot(shape.vertices[0]);
double max = min;
for (int i = 1; i < shape.vertices.length; ++i) {// NOTE: the axis must be normalized to get accurate projectionsdouble p = axis.dot(shape.vertices[i]);if (p < min) {min = p;} else if (p > max) {max = p;}
}
Projection proj = new Projection(min, max);
return proj;
4. 计算MTV
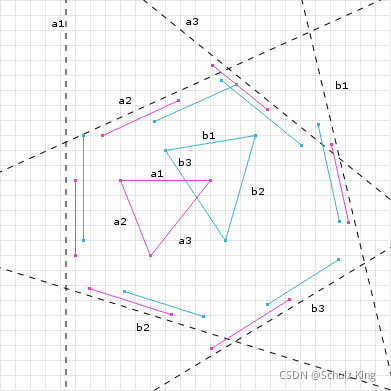
如下图所示,两个凸多边形在边 b 3 b3 b3法向量(分离轴)上重叠的区域最少,沿此方向可以移动最小的距离使两个碰撞的凸多边形分开,此向量方向和移动的距离叫做 M T V MTV MTV。
double overlap = DBL_MAX;
Axis samllest = null;
Axis[] axes1 = shape1.getAxes();
Axis[] axes2 = shape2.getAxes();
for (int i = 0; i < axes1.length; ++i) {Axis axis = axies1[i];Projection p1 = shape1.project(axis);Projection p2 = shape2.project(axis);if (!p1.overlop(p2) {return flase;} else {double o = p1.getOverlap(p2);if (o < overlap) {overlap = o;samllest = axis;}}
}
for (int i = 0; i < axes2.length; ++i) {Axis axis = axes2[i];Projection p1 = shape1.project(axis);Projection p2 = shape2.project(axis);if (!p1.overlap(p2)) {retrun false;} else {double o = p1.getOverlap(p2);if (o < overlap) {overlap = o;smallest = axis;}}
}
MTV mtv = new MTV(smallset, overlap);
return ture;

if (!p1.overlap(p2)) {retrun false;
} else {double o = p1.getOverlap(p2);// check for containmentif (p1.contains(p2) || p2.contains(p1)) {// get the overlap plus the distance from the minimum end pointsdouble mins = abs(p1.min - p2.min);double maxs = abs(p1.amx - p2.max);// NOTE: depending on which is smaller you may need to negate the separating axis!!if (mins < maxs) {o += mins;axis = -axis; // negate the separating axis} elst {o += maxs;}}// check for minimunif (o < overlap) {overlap = o;smallest = axis;}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!